Difference between revisions of "Jobsolescence"
(more bits; saving) |
(→Links) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Jobsolescence: why chronic unemployment is the new normal, and what to do about it''' | '''Jobsolescence: why chronic unemployment is the new normal, and what to do about it''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''a traveler's guide to the new economic landscape'' | ||
| + | ==Outline== | ||
| + | * Introduction | ||
| + | * The Current Situation | ||
| + | ** How We Got Here | ||
| + | ** Surreal Economic Disparity | ||
| + | ** The Employment Ethic | ||
| + | * New Models and How to Build Them | ||
| + | ** The Value Ethic | ||
| + | ** Won't People Be Bored?: Post-Employment Careers | ||
| + | ** Fair Share | ||
| + | ** Corporate Rehabilitation | ||
| + | ** Copying Things: The Sincerest Form of Flattery | ||
| + | ** The Tax-Hater's Guide to Universal Welfare | ||
| + | * Jobsolescence and the Free Market | ||
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
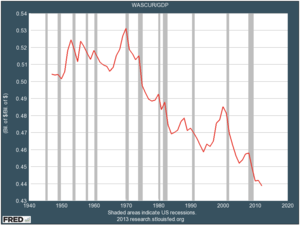
| − | We are faced now with chronic unemployment in all areas of society | + | [[File:Screen shot 2013-04-11 at 9.58.53 am.png|300px|thumb|Total wages as a portion of GDP have fallen steadily since the 1950s.]] |
| + | As automation increases efficiency, fewer people are needed to create the same wealth -- which would be good, except that the owners of the resources have been gaining all the benefit, and have become increasingly stingy about sharing it even as it accumulates to absurd heights. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We are faced now with chronic unemployment in all areas of society -- but what most people don't seem to realize is that "unemployment" isn't the problem; economic inequity is the problem. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We have what is supposed to be a democracy -- rule of, by, and for the people, where everyone's opinion counts the same as anyone else's. We now have an oligarchy ruling over an increasinly marginalized underclass, speeding headlong toward technologically-gilded feudalism. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When most people could find jobs earning a living wage, economic inequity was minimized by the constant redistribution of wealth from factory-owners to employees. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The era of high employment is over. The work ethic -- where "work" is taken to mean "employment" -- has outlived its usefulness. If we're going to emerge from the current crisis with anythin resembling a happy society, we have to change a number of basic things about it -- including the way we think about work, the way we allocate and distribute resources, and some basic assumptions about what an "economy" is -- because automation has completely transformed the reality of what work needs to be done. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We need new ways of allocating society's core wealth, and we need new guiding ethics by which people can gauge the value of their contributions to it. People are too many, employment opportunities too few, and basic resources too plentiful for society to insist that a decent living must require hard work. | ||
| + | ==The Current Situation== | ||
| + | ===How We Got Here=== | ||
| + | When most people could find jobs earning a living wage, the general tendency for wealth to concentrate in the hands of the factory owners was far better counteracted by the need to hire employees to run those factories. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Automation increases the wealth generation potential per employee. That means fewer employees generating the same amount of product -- which means either more profit for the owner, or higher wages for the workers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The owners started noticing this effect sometime around the beginning of the twentieth century, and realized they had a dilemma. If they paid their employees more, then they would make less profit than if they simply kept the resulting gains. On the other hand, if they ''didn't'' raise wages, then the supply of money out "in the wild" -- in the economy at large -- would be less, and people would be less able to afford to buy what the factories were making, so the owners would again make less profit. | ||
| + | |||
| + | They ultimately solved the problem by creating more things to spend money on, thus expanding the "owner" class. They also discovered ways to convince people to buy more of what they were already buying, and to believe they needed things that they didn't really need -- and thus the commercial propaganda industry (also known as "advertising") was born, creating yet more employment without ceding the least bit of control over the essential machinery of production. | ||
| + | ===Surreal Economic Disparity=== | ||
| + | Most people don't realize just how extreme the situation is. We have become so astonishingly wealthy as a country that even the much smaller piece of pie that most of us are getting seems reasonable, since the pie is so much bigger. The fact that our slice is nonetheless shrinking a little can be chalked up to bad luck, because we simply have no intuitive grasp of just how big the pie has gotten. | ||
| + | ===The Employment Ethic=== | ||
| + | As difficult as it will be for many people to accept the need to reorganize society, it will be much more difficult for some to accept the end of the employment ethic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When this country was founded, and the ethical foundations of our culture were being worked out by our forebears, work was plentiful and people were scarce. Food was also scarce, but farmland was plentiful. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a result of these conditions, the "work ethic" was a formula for success, and became part of our cultural identity. When finished products are scarce -- be they food, clothing, farm implements, or anything ready to use or consume -- it makes sense to say that anyone who is ''able'' to work ''should'' work. When the means of creating finished products are plentiful, there's no excuse for not becoming involved in such work. Anyone who could but would not participate is effectively "free-riding" on the labor of others, and was rightly regarded as a parasite. Work was legitimacy -- and thus the American work ethic took root. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As labor shifted from being primarily agricultural to factory work to being primarily service-oriented, the work ethic shifted from physical outdoor labor to include whatever brought in a regular income -- even though the actual work involved was not, in many cases, actually helping to create wealth (i.e. feed, clothe, or house anyone); the mere fact of ''being paid'' became the badge of legitimacy. | ||
| + | ==New Models and How to Build Them== | ||
| + | ===The Value Ethic=== | ||
| + | When people were scarce and opportunities for work were everywhere, it made sense for the ethic to say "don't come to me looking for handouts -- go do some work! Get a job!" | ||
| + | |||
| + | When people are everywhere and opportunities for work are scarce, the ethic needs to appreciate that having work is something that not everyone can have -- a prized achievement. We've seen the beginnings of social evolution towards this in the antipathy towards immigrants "stealing our jobs", but this isn't really acknowledging the change; it's trying to pretend that it's a temporary problem caused by an out-group. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The new ethic needs to acknowledge that: | ||
| + | * every human has a right to share in the massive surplusses our civilization creates | ||
| + | * any job is better done by someone who wants it to be done than by someone who just does it for the money | ||
| + | * labor for the common good is worthy of respect | ||
| + | * laboring for personal gain is not inherently virtuous | ||
| + | * making profit for others is not inherently virtuous | ||
| + | * there is virtue in any work well done | ||
| + | |||
| + | If this needs to be expressed in a territorial kind of way, it should be something more like "take your fair share, not my job". | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | There's still plenty of work, but less and less of it is the kind of work that someone is willing to pay someone else to do. More and more of it is the kind of work that benefits society at large, often tremendously, but does not benefit any individual actor (person or company) enough to make it worth that actor's investment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Perhaps more importantly, the results of the new work tend to be the sort of thing that is easily copied, easily transported -- writing, music, blueprints, software. I'll discuss the effects of this change in more detail in another chapter (Copying Things) -- but suffice it to say that the obstacle is no longer copying and distribution; one person, acting alone, can write and distribute works that can help or entertain millions of people. | ||
| + | ===Won't People Be Bored?: Post-Employment Careers=== | ||
| + | ===Fair Share=== | ||
| + | The public revenue-share has been declining for many decades, but we didn't really notice it -- because ''overall wealth'' was increasing, and a smaller share of a larger pie still looks pretty good -- until significant numbers of people started finding themselves abruptly kicked out of the walled city. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Clearly this is a problem, but so far the only solution that has been anywhere near the table is the idea that the government needs to take care of the unemployed -- although not ''all'' of the unemployed, and not ''indefinitely,'' because of the usual corporate propaganda encouraging everyone to think that unemployment is basically sinful -- something that people gravitate towards unless deterred by punishment, and something that anyone can avoid if they just try. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is an awkward solution at best. A better solution would be one which more closely modeled our basic ethics as civilized humans: everyone should be taken care of to the extent that we can afford to do so | ||
| + | ===Corporate Rehabilitation=== | ||
| + | ===Copying Things: The Sincerest Form of Flattery=== | ||
| + | In one way, individuals now have far more power to do good than at any previous time in history. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Through software, one person can solve a problem for millions of other people. Our traditional economic model for making a living at software, however, requires each solution to be kept secret and only revealed to the one entity who has agreed to pay for the necessary work. This drastically reduces the benefit, while simultaneously putting a much greater burden on each payer; consequently, they must make a lot of money from the solution, or else it's not worth buying. A lot of software simply doesn't get written, or properly maintained, under this model -- and software vendors have an incentive to build in defects and shortcomings so that customers will want to keep buying upgrades, thus ensuring income even if the company never actually solves any new problems ever again. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Things like writing, music, blueprints, and software used to be much harder to copy, requiring the expenditure of physical supplies (paper, vinyl) and physical transportation to distribute. It made sense to say that the creator should receive some share of the final sale price, as this would help pay for their labor in creating it and allow a talented creator to devote more time to creating additional works, thus benefiting society even more. | ||
| − | + | I'll refer to this model as "copyright", though it also includes patents. | |
| − | + | As the technical barriers to copying and distribution have crumbled -- the cost going from a matter of dollars per copy (for a book or record) to pennies or even fractions of a penny{{l/foot|1}} -- and it has become easier for individuals to copy without the help of large businesses with expensive equipment, those whose business models were built around "copyright" have felt compelled to place artificial barriers against copying. A large business can much more easily be held accountable for selling copies of a work than an individual can be held accountable for giving away copies. | |
| + | ===The Tax-Hater's Guide to Universal Welfare=== | ||
| − | + | ==Jobsolescence and the Free Market== | |
| + | The phrase "free market" actually has two possible meanings: free-as-in-unconstrained and free-as-in-choice. A free-unconstrained market is one in which no external coercion is applied to anyone within the market; a free-choice market is one in which all participants not only have multiple options in any given transaction, but have no constraints on which options they can choose. | ||
| + | Neither one really exists; they are both ideals. When people advocate either one, what they are actually suggesting is that we should support a regulatory environment intended to encourage the economy to move in that direction. Worse, free-unconstrained advocates like to conflate the two types of "free", selling us their dystopian neofeudalism wrapped in a package suggesting the much happier circumstance of free-choice. This is why they never clarify which one they are talking about. | ||
| + | Jobsolescence was largely the creation of a free-unconstrained market in which employers increased the efficiency of their operations over time, gradually reducing their need for employees -- while working to create a regulatory environment in which most people ''have'' to work in order to live at a reasonable level, by sharply eroding the government-provided social supports which would have helped those for whom jobs are simply no longer available. This in turn gives employers the upper hand in negotiations with employees, allowing businesses the benefit of a large pool of applicants for most jobs, from which they can pick only the very "best" -- while those who don't make the cut are not only left without adequate income, but are socially encouraged to feel unworthy as well. | ||
| + | What we ''want'', of course, is not a ''free-unconstrained'' market but a ''free-choice'' market, in which everyone has enough income to choose those goods and services with the best value, rather than always having to go with the "cheapest" (which often end up costing more in the long run) -- and in which employees can choose whether to work for a given employer, rather than feeling compelled to work for the first place that offers them a job. | ||
| + | This latter choice is an important check on corporate ethical behavior. If your employer is behaving unethically but your current job is your only life-line to being able to pay your bills, practical considerations tend to override ethical ones (indeed, we are often encouraged to "set our principles aside" for the sake of financial stability and our families and loved ones -- "Think of the children!"). | ||
==Discarded bits== | ==Discarded bits== | ||
The American economy did eventually recover from the 2007 crash, but unemployment stayed high. | The American economy did eventually recover from the 2007 crash, but unemployment stayed high. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 107: | ||
On the Right, "job creator" became a synonym for "large company" in order to justify continuing the failed policy of trickle-down economics. The Left, a bit more realistically, focused on the need for aid to the unemployed -- but even they regarded it as a temporary measure, a band-aid solution, while the Right considered even temporary measures as a gateway drug to "dependency" on "government hand-outs" (something they were all too willing to give to the aforementioned large corporations). | On the Right, "job creator" became a synonym for "large company" in order to justify continuing the failed policy of trickle-down economics. The Left, a bit more realistically, focused on the need for aid to the unemployed -- but even they regarded it as a temporary measure, a band-aid solution, while the Right considered even temporary measures as a gateway drug to "dependency" on "government hand-outs" (something they were all too willing to give to the aforementioned large corporations). | ||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | {{t/foot|1|A blank DVD costs about 30 cents, which is only slightly less than the cost of keeping its contents on a hard drive. The reverse will soon be true. A blank CD costs about the same -- but its contents can be stored for less than a dime's worth of hard drive space (based on the price of a 1 terabyte drive, which is now well under $100). If compressed to MP3 format, that goes down to less than a penny. A typical novel takes up less than one ''hundredth'' of a penny's worth of hard drive space, and can be copied from one side of the world to the other in a matter of seconds.}} | ||
| + | ==Related== | ||
| + | * [[post-employment economy]] | ||
| + | ==Links== | ||
| + | * [[issuepedia:Jobsolescence|Issuepedia]] | ||
| + | * [https://plus.google.com/s/%23jobsolescence #jobsolescence] posts on G+ | ||
| + | * '''2012-11-21''' [http://www.businessinsider.com/rich-countries-producing-too-few-grads-2012-11 McKinsey Predicts The War For Talent Will Go Nuts By 2020]: if we're producing too few college grads, why do companies insist on hiring college grads? Also, why don't they offer to help pay for college? | ||
| + | * '''2012-12-31''' [http://blog.p2pfoundation.net/working-for-the-commons-after-the-end-of-the-labor-market/2012/12/31 Working for the commons after the end of the labor market] | ||
| + | * '''2013-03-30''' [http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/wonkblog/wp/2013/03/30/ow-an-anti-rentier-agenda-might-bring-liberals-conservatives-together/ How an anti-rentier agenda might bring liberals, conservatives together] | ||
| + | * '''2013-06-03''' [http://truth-out.org/opinion/item/16735-a-better-way-to-tax-the-multinationals A Better Way to Tax the Multinationals] | ||
| + | * '''2013-06-06''' [http://www.businessinsider.com/mckinsey-disruptive-technology-report-2013-6 12 Technologies That Are Improving At Insane Speeds] | ||
| + | * '''2013-06-12''' [http://www.shareable.net/blog/a-new-book-offers-a-new-american-revolution Solidarity Economy: The Next American Revolution?]: book review of ''What Then Must We Do?'' by [[Gar Alperovitz]] | ||
| + | * '''2013-06-22''' [https://plus.google.com/u/0/117903011098040166012/posts/e1bGyG5ZKaM on ''Some Guides for Feminine Energy'']: even in 1915, it was clear to some that there just wasn't as much work that ''needed doing'' as there once had been. | ||
| + | ===Woozle posts=== | ||
| + | * '''2012-09-13''' [https://plus.google.com/102282887764745350285/posts/JKJSiko5c8Y increased efficiency in big business always means creating more economic output with fewer people] | ||
| + | * '''2013-01-26''' [https://plus.google.com/102282887764745350285/posts/RKpy2Dij1oC Jobsolescence on ''60 Minutes''] | ||
| + | * '''2013-05-23''' [https://plus.google.com/u/0/102282887764745350285/posts/crxFe6T6TNs Rising "disability" claims are another consequence of #jobsolescence.] | ||
| + | ===Non-Woozle posts=== | ||
| + | * '''2013-07-08''' [https://plus.google.com/u/0/112224011593759485232/posts/M5keDdGywGD a commenter objects to redistribution] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:46, 15 July 2013
Jobsolescence: why chronic unemployment is the new normal, and what to do about it
a traveler's guide to the new economic landscape
Outline
- Introduction
- The Current Situation
- How We Got Here
- Surreal Economic Disparity
- The Employment Ethic
- New Models and How to Build Them
- The Value Ethic
- Won't People Be Bored?: Post-Employment Careers
- Fair Share
- Corporate Rehabilitation
- Copying Things: The Sincerest Form of Flattery
- The Tax-Hater's Guide to Universal Welfare
- Jobsolescence and the Free Market
Introduction
As automation increases efficiency, fewer people are needed to create the same wealth -- which would be good, except that the owners of the resources have been gaining all the benefit, and have become increasingly stingy about sharing it even as it accumulates to absurd heights.
We are faced now with chronic unemployment in all areas of society -- but what most people don't seem to realize is that "unemployment" isn't the problem; economic inequity is the problem.
We have what is supposed to be a democracy -- rule of, by, and for the people, where everyone's opinion counts the same as anyone else's. We now have an oligarchy ruling over an increasinly marginalized underclass, speeding headlong toward technologically-gilded feudalism.
When most people could find jobs earning a living wage, economic inequity was minimized by the constant redistribution of wealth from factory-owners to employees.
The era of high employment is over. The work ethic -- where "work" is taken to mean "employment" -- has outlived its usefulness. If we're going to emerge from the current crisis with anythin resembling a happy society, we have to change a number of basic things about it -- including the way we think about work, the way we allocate and distribute resources, and some basic assumptions about what an "economy" is -- because automation has completely transformed the reality of what work needs to be done.
We need new ways of allocating society's core wealth, and we need new guiding ethics by which people can gauge the value of their contributions to it. People are too many, employment opportunities too few, and basic resources too plentiful for society to insist that a decent living must require hard work.
The Current Situation
How We Got Here
When most people could find jobs earning a living wage, the general tendency for wealth to concentrate in the hands of the factory owners was far better counteracted by the need to hire employees to run those factories.
Automation increases the wealth generation potential per employee. That means fewer employees generating the same amount of product -- which means either more profit for the owner, or higher wages for the workers.
The owners started noticing this effect sometime around the beginning of the twentieth century, and realized they had a dilemma. If they paid their employees more, then they would make less profit than if they simply kept the resulting gains. On the other hand, if they didn't raise wages, then the supply of money out "in the wild" -- in the economy at large -- would be less, and people would be less able to afford to buy what the factories were making, so the owners would again make less profit.
They ultimately solved the problem by creating more things to spend money on, thus expanding the "owner" class. They also discovered ways to convince people to buy more of what they were already buying, and to believe they needed things that they didn't really need -- and thus the commercial propaganda industry (also known as "advertising") was born, creating yet more employment without ceding the least bit of control over the essential machinery of production.
Surreal Economic Disparity
Most people don't realize just how extreme the situation is. We have become so astonishingly wealthy as a country that even the much smaller piece of pie that most of us are getting seems reasonable, since the pie is so much bigger. The fact that our slice is nonetheless shrinking a little can be chalked up to bad luck, because we simply have no intuitive grasp of just how big the pie has gotten.
The Employment Ethic
As difficult as it will be for many people to accept the need to reorganize society, it will be much more difficult for some to accept the end of the employment ethic.
When this country was founded, and the ethical foundations of our culture were being worked out by our forebears, work was plentiful and people were scarce. Food was also scarce, but farmland was plentiful.
As a result of these conditions, the "work ethic" was a formula for success, and became part of our cultural identity. When finished products are scarce -- be they food, clothing, farm implements, or anything ready to use or consume -- it makes sense to say that anyone who is able to work should work. When the means of creating finished products are plentiful, there's no excuse for not becoming involved in such work. Anyone who could but would not participate is effectively "free-riding" on the labor of others, and was rightly regarded as a parasite. Work was legitimacy -- and thus the American work ethic took root.
As labor shifted from being primarily agricultural to factory work to being primarily service-oriented, the work ethic shifted from physical outdoor labor to include whatever brought in a regular income -- even though the actual work involved was not, in many cases, actually helping to create wealth (i.e. feed, clothe, or house anyone); the mere fact of being paid became the badge of legitimacy.
New Models and How to Build Them
The Value Ethic
When people were scarce and opportunities for work were everywhere, it made sense for the ethic to say "don't come to me looking for handouts -- go do some work! Get a job!"
When people are everywhere and opportunities for work are scarce, the ethic needs to appreciate that having work is something that not everyone can have -- a prized achievement. We've seen the beginnings of social evolution towards this in the antipathy towards immigrants "stealing our jobs", but this isn't really acknowledging the change; it's trying to pretend that it's a temporary problem caused by an out-group.
The new ethic needs to acknowledge that:
- every human has a right to share in the massive surplusses our civilization creates
- any job is better done by someone who wants it to be done than by someone who just does it for the money
- labor for the common good is worthy of respect
- laboring for personal gain is not inherently virtuous
- making profit for others is not inherently virtuous
- there is virtue in any work well done
If this needs to be expressed in a territorial kind of way, it should be something more like "take your fair share, not my job".
There's still plenty of work, but less and less of it is the kind of work that someone is willing to pay someone else to do. More and more of it is the kind of work that benefits society at large, often tremendously, but does not benefit any individual actor (person or company) enough to make it worth that actor's investment.
Perhaps more importantly, the results of the new work tend to be the sort of thing that is easily copied, easily transported -- writing, music, blueprints, software. I'll discuss the effects of this change in more detail in another chapter (Copying Things) -- but suffice it to say that the obstacle is no longer copying and distribution; one person, acting alone, can write and distribute works that can help or entertain millions of people.
Won't People Be Bored?: Post-Employment Careers
The public revenue-share has been declining for many decades, but we didn't really notice it -- because overall wealth was increasing, and a smaller share of a larger pie still looks pretty good -- until significant numbers of people started finding themselves abruptly kicked out of the walled city.
Clearly this is a problem, but so far the only solution that has been anywhere near the table is the idea that the government needs to take care of the unemployed -- although not all of the unemployed, and not indefinitely, because of the usual corporate propaganda encouraging everyone to think that unemployment is basically sinful -- something that people gravitate towards unless deterred by punishment, and something that anyone can avoid if they just try.
This is an awkward solution at best. A better solution would be one which more closely modeled our basic ethics as civilized humans: everyone should be taken care of to the extent that we can afford to do so
Corporate Rehabilitation
Copying Things: The Sincerest Form of Flattery
In one way, individuals now have far more power to do good than at any previous time in history.
Through software, one person can solve a problem for millions of other people. Our traditional economic model for making a living at software, however, requires each solution to be kept secret and only revealed to the one entity who has agreed to pay for the necessary work. This drastically reduces the benefit, while simultaneously putting a much greater burden on each payer; consequently, they must make a lot of money from the solution, or else it's not worth buying. A lot of software simply doesn't get written, or properly maintained, under this model -- and software vendors have an incentive to build in defects and shortcomings so that customers will want to keep buying upgrades, thus ensuring income even if the company never actually solves any new problems ever again.
Things like writing, music, blueprints, and software used to be much harder to copy, requiring the expenditure of physical supplies (paper, vinyl) and physical transportation to distribute. It made sense to say that the creator should receive some share of the final sale price, as this would help pay for their labor in creating it and allow a talented creator to devote more time to creating additional works, thus benefiting society even more.
I'll refer to this model as "copyright", though it also includes patents.
As the technical barriers to copying and distribution have crumbled -- the cost going from a matter of dollars per copy (for a book or record) to pennies or even fractions of a penny1 -- and it has become easier for individuals to copy without the help of large businesses with expensive equipment, those whose business models were built around "copyright" have felt compelled to place artificial barriers against copying. A large business can much more easily be held accountable for selling copies of a work than an individual can be held accountable for giving away copies.
The Tax-Hater's Guide to Universal Welfare
Jobsolescence and the Free Market
The phrase "free market" actually has two possible meanings: free-as-in-unconstrained and free-as-in-choice. A free-unconstrained market is one in which no external coercion is applied to anyone within the market; a free-choice market is one in which all participants not only have multiple options in any given transaction, but have no constraints on which options they can choose.
Neither one really exists; they are both ideals. When people advocate either one, what they are actually suggesting is that we should support a regulatory environment intended to encourage the economy to move in that direction. Worse, free-unconstrained advocates like to conflate the two types of "free", selling us their dystopian neofeudalism wrapped in a package suggesting the much happier circumstance of free-choice. This is why they never clarify which one they are talking about.
Jobsolescence was largely the creation of a free-unconstrained market in which employers increased the efficiency of their operations over time, gradually reducing their need for employees -- while working to create a regulatory environment in which most people have to work in order to live at a reasonable level, by sharply eroding the government-provided social supports which would have helped those for whom jobs are simply no longer available. This in turn gives employers the upper hand in negotiations with employees, allowing businesses the benefit of a large pool of applicants for most jobs, from which they can pick only the very "best" -- while those who don't make the cut are not only left without adequate income, but are socially encouraged to feel unworthy as well.
What we want, of course, is not a free-unconstrained market but a free-choice market, in which everyone has enough income to choose those goods and services with the best value, rather than always having to go with the "cheapest" (which often end up costing more in the long run) -- and in which employees can choose whether to work for a given employer, rather than feeling compelled to work for the first place that offers them a job.
This latter choice is an important check on corporate ethical behavior. If your employer is behaving unethically but your current job is your only life-line to being able to pay your bills, practical considerations tend to override ethical ones (indeed, we are often encouraged to "set our principles aside" for the sake of financial stability and our families and loved ones -- "Think of the children!").
Discarded bits
The American economy did eventually recover from the 2007 crash, but unemployment stayed high.
This is merely the capstone on a series of events beginning sometime during the late Industrial Revolution
"Job creation" was the buzz-phrase of the elections in 2008, 2010, and 2012.
On the Right, "job creator" became a synonym for "large company" in order to justify continuing the failed policy of trickle-down economics. The Left, a bit more realistically, focused on the need for aid to the unemployed -- but even they regarded it as a temporary measure, a band-aid solution, while the Right considered even temporary measures as a gateway drug to "dependency" on "government hand-outs" (something they were all too willing to give to the aforementioned large corporations).
Notes
1. A blank DVD costs about 30 cents, which is only slightly less than the cost of keeping its contents on a hard drive. The reverse will soon be true. A blank CD costs about the same -- but its contents can be stored for less than a dime's worth of hard drive space (based on the price of a 1 terabyte drive, which is now well under $100). If compressed to MP3 format, that goes down to less than a penny. A typical novel takes up less than one hundredth of a penny's worth of hard drive space, and can be copied from one side of the world to the other in a matter of seconds.
Related
Links
- Issuepedia
- #jobsolescence posts on G+
- 2012-11-21 McKinsey Predicts The War For Talent Will Go Nuts By 2020: if we're producing too few college grads, why do companies insist on hiring college grads? Also, why don't they offer to help pay for college?
- 2012-12-31 Working for the commons after the end of the labor market
- 2013-03-30 How an anti-rentier agenda might bring liberals, conservatives together
- 2013-06-03 A Better Way to Tax the Multinationals
- 2013-06-06 12 Technologies That Are Improving At Insane Speeds
- 2013-06-12 Solidarity Economy: The Next American Revolution?: book review of What Then Must We Do? by Gar Alperovitz
- 2013-06-22 on Some Guides for Feminine Energy: even in 1915, it was clear to some that there just wasn't as much work that needed doing as there once had been.
Woozle posts
- 2012-09-13 increased efficiency in big business always means creating more economic output with fewer people
- 2013-01-26 Jobsolescence on 60 Minutes
- 2013-05-23 Rising "disability" claims are another consequence of #jobsolescence.
Non-Woozle posts
- 2013-07-08 a commenter objects to redistribution